Copying Plants & Other Blocks: How To (and How Not To)
Issue
You want to copy blocks from your drawing to place in either the same drawing or a different one. You can use the following methods for copying several types of blocks, including:
- Irrigation equipment
- Plants
- Labels and callouts
- Site objects (Site Amenities, Elevation Graphics, Plan Graphics, etc.)
Solution
Method #1 (copying plants and/or labels within a single drawing)
Quick video
Our XCOPY and XCORO tools provide the best methods for copying plants and labels within the same drawing.
XCOPY runs the copy portion of the AutoCAD Move, Copy, Rotate (MOCORO) command, while XCORO runs the copy and rotate portions of the same command. If you need to rotate the copied labels, use XCORO. If not, use XCOPY.
Important: When using XCOPY or XCORO to copy plants and labels, use each tool on both the plant and its associated label at the same time. If you use XCOPY or XCORO on plants and labels separately, they will lose their associations.
Method #2
The quickest and easiest way to copy and paste blocks between drawings is to use the standard copy and paste keyboard commands. (You can also use these commands for copying and pasting plants and labels within a single drawing, although our XCOPY and XCORO tools are much more useful.)
To copy one or more blocks, press CTRL + C (Windows keyboard) or Command + C (Mac keyboard). The Command line will prompt you to Select objects. Click the block(s) you want to copy. You can also draw a window encompassing several objects. When finished copying, press Enter.
To paste the blocks, press CTRL + V (Windows keyboard) or Command + V (Mac keyboard). The Command line will prompt you to Specify insertion point. Click a location in your drawing to place the blocks.
Method #3
You'll only need to use this method if your copying Clipboard is not available – for example, when you need to copy blocks across machines or offices. This method also creates a digital trail for copied items, which you may prefer.
Method #3 involves using the CAD WBLOCK (Write Block) command.
Type WBLOCK in the Command line. The Write Block dialog box will open. Under Source, select Objects. Then click OK.
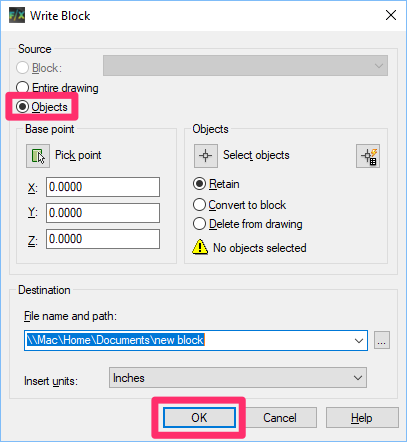
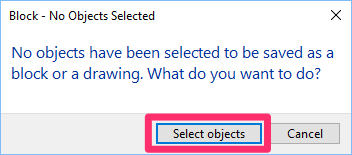
If you haven't yet selected the object(s) to copy, you'll see a No Objects Selected message. Click Select Objects.
Click the block(s) you want to copy. You can also draw a window encompassing several objects. When finished copying, press Enter.
To paste the blocks, open the drawing where you want to insert the blocks. Type INSERT in the Command line.
The Insert dialog box will open. Specify an Insertion Point, setting the X and Y coordinates to the location of your choice.
Click OK.
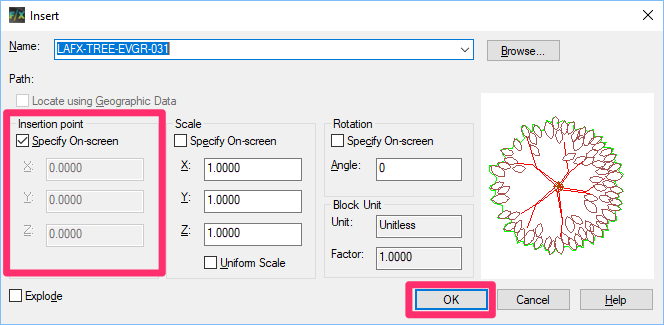
The blocks will appear in your drawing. Confirm that all blocks you've inserted are in the correct locations.
If you want to edit the blocks, you can then explode them:
Type EXPLODE in the Command line and press Enter.
You'll be prompted to Select objects. Select the block or blocks you'd like to explode. If desired, you can draw a window to select multiple blocks.
Press Enter. The blocks will be exploded and editable.
How Not to Copy Blocks – DO NOT Use the AutoCAD Copy Command
A note of caution: Do not use the AutoCAD Copy command to copy blocks. The Copy command essentially creates a "clone" of the original block, pulling the exact data associated with it and applying that identical data to the new copy.
For example, if you use the CAD Copy command to copy and paste a piece of irrigation equipment, the system won't just think you've placed a new piece of equipment of the same type – it will think you've placed that exact same piece of equipment, with all the same piping and flow data. This will in turn create problems with your overall irrigation system.
In the case of planting, using the Copy command to copy a plant or its label will create problems because they system will think you have two versions of the exact same plant in your drawing. The labeling system will become confused, and your plant counts will be off.
Thus, if you want to copy and paste a block, you'll need to use one of the two methods described above.







